In this article, we’ll discuss angular contact ball bearings.
There are several types of ball bearings, including deep groove ball bearings, thrust bearings, and angular contact ball bearings. They differ in the applications and environments where they are used, particularly in the types of loads they can handle:
| Type of Bearing | Load Characteristics |
|---|---|
| Deep groove ball bearings | Support both thrust (axial) loads parallel to the shaft and radial loads perpendicular to the shaft, in both directions. The most common general-purpose bearing type. |
| Thrust bearings | Support thrust loads in one direction only. |
| Angular contact bearings | Support radial loads and thrust loads in one direction. |
Angular contact bearings look similar to deep groove ball bearings, but their performance differs due to the raceway design.
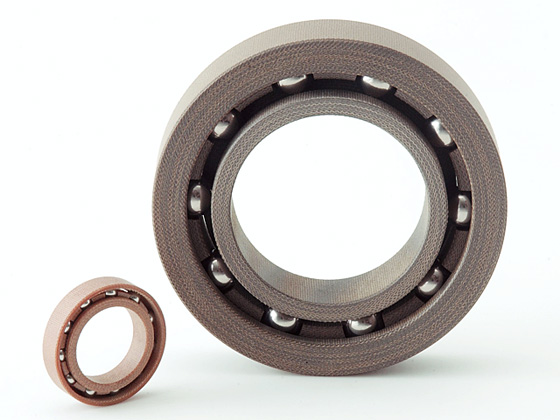

Angular Contact Ball Bearings
Structure and Contact Angle
Deep groove ball bearings consist of an inner ring, an outer ring (the raceways), a cage, and balls. Angular contact bearings use the same components, but the groove shape is different.
In deep groove bearings, the grooves are symmetrical about the centerline. In angular contact bearings, the grooves are offset at an angle so that forces are transmitted from one groove to the other along a diagonal path. This offset is called the contact angle.
A larger contact angle allows the bearing to support greater thrust loads, but it also reduces the maximum permissible rotational speed. Standard contact angles are typically 15°, 30°, and 40°, although some manufacturers also offer 25° or follow different standards.
Types of Angular Contact Bearings
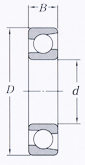
- Single-row angular contact bearings: Appear similar to deep groove ball bearings.
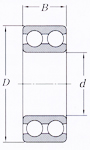
- Double-row angular contact bearings: Combine two single-row bearings into a single integrated inner and outer ring.
|
Single-row angular contact bearings Appear similar to deep groove ball bearings. |
|
Double-row angular contact bearings Combine two single-row bearings into a single integrated inner and outer ring. In many cases, the double-row type is more cost-effective than using two single-row bearings together. |
Paired angular contact bearings are also available, in which two single-row bearings are mounted together. Their performance depends on the pairing arrangement, which is chosen according to the application requirements.
Choosing the Right Bearing
If a bearing must handle loads from both radial and thrust directions, a single-row angular contact bearing is not always the best option. The choice between deep groove and angular contact bearings depends on the operating conditions.
As noted, deep groove bearings can handle both radial and thrust loads, but they are less suitable for high thrust loads. Angular contact bearings, thanks to their contact angle, can handle higher thrust loads than deep groove bearings, but only in one direction.
Careful selection is essential to ensure optimal performance.
Special Environments for Plastic Angular Contact Bearings
Kashima Bearings manufactures angular contact bearings from engineering plastics. Unlike metal bearings, they can be used in environments where corrosion, magnetism, or lubrication are concerns, such as:
- Underwater: No risk of rust.
- Chemical solutions: Corrosion-resistant.
- High-temperature environments: Heat-resistant plastic versions available; no grease required, so no risk of grease drying out.
- Non-magnetic environments: Safe for use near metal detectors.
- Electrical insulation: Suitable where conductivity must be avoided.
Examples of Use
- Plating equipment where copper sheets pass vertically between rollers.
- Transfer components in semiconductor-related equipment where thrust loads are also applied.
Contact Us
We can assist from material selection onward. If you have issues with bearings in special environments or questions about plastics, feel free to contact us — even for advice only.
Kashima Bearings manufactures a wide range of plastic bearings and has extensive machining expertise. If you have any difficulties, please contact us.

